Marketplace Pulse recently released its annual review of the U.S. e-commerce market for 2024, focusing on the market disruption brought by Chinese platforms such as Temu, Amazon's response strategy, the slowdown in e-commerce growth after the pandemic, and the application prospects of artificial intelligence in the future of shopping.
I. China's e-commerce to promote the change of the global e-commerce landscape
Marketplace Pulse notes that in 2024, Shein and Temu are in the spotlight. The trend has grown over the years as goods made in China are sold directly to global consumers through Chinese companies. The current lack of U.S. tariffs on small items under $800 presents a huge opportunity for Chinese e-commerce platforms, while also posing a challenge for local retailers.
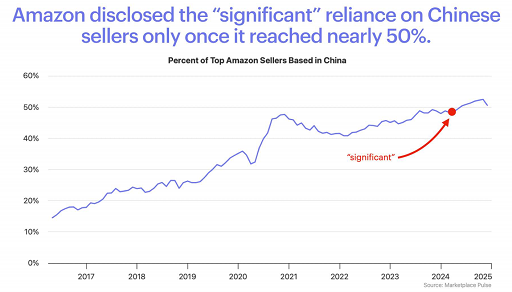
Before Shein and Temu came along, Amazon had become an important platform for Chinese sellers to enter Western markets. In February, Amazon's annual 10-K report filed with the SEC showed that Chinese sellers accounted for a significant percentage of its third-party seller services and advertising revenue. In addition, Chinese suppliers also make up a large share of Amazon's parts and finished products supply chain. Chinese sellers now account for more than 50% of Amazon's top sellers.
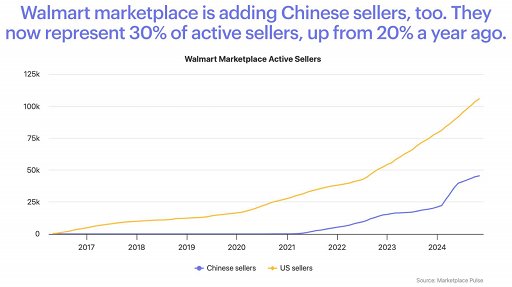
At the same time, Walmart is also accelerating its efforts to attract Chinese sellers. While U.S. sellers still dominate, Chinese sellers' share of active sellers on Walmart's platform has climbed to 30 percent from 20 percent a year ago, showing the growing influence of Chinese sellers.
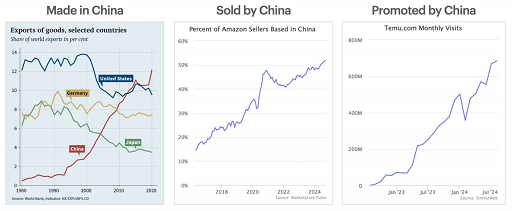
The rise of "Made in China" began in the 1980s, when China's share of exports of goods was much lower than that of the United States, Germany and Japan. By around 2010, China had approached the United States as a major force in global manufacturing and eventually surpassed it. Since then, platforms such as Amazon have promoted further transformation, and the proportion of Chinese cross-border sellers has continued to rise, completing the evolution from "made in China" to "sold in China".
Now, with the rise of new platforms, the e-commerce market has ushered in a third evolution - "driven by China." Temu, in particular, has continued to rise in popularity since its launch, with more than 600 million monthly visits. Overall, from manufacturing to sales to platform dominance, China is gradually leading the transformation of the e-commerce landscape and having a profound impact on the retail industry.
II.The rise of e-commerce in China: Regulatory changes and consumer attitudes

Temu's rapid rise has made it the second most visited e-commerce platform in the world after Amazon two years after its launch. At the same time, Shein quickly gained attention in the global market with its "faster than fast fashion" model. As the business expanded, the two platforms gradually adjusted their strategies. Shein has built factories in Turkey and other places, and has improved storage capacity in Europe and the United States, and Temu has achieved more than 50% of orders shipped through local warehouses in the United States. Although the sellers are still dominated by Chinese suppliers, this localized layout is gradually reducing the logistics delays and regulatory risks faced by cross-border e-commerce.
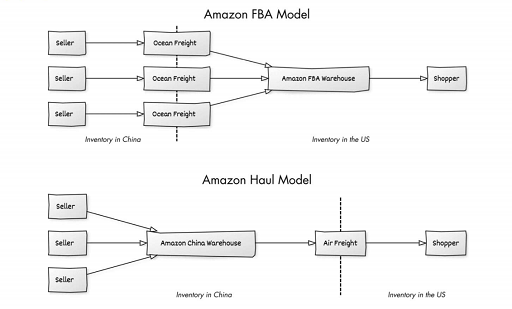
In the face of Temu's strong rise, Amazon launched low-price mall Amazon Haul, aiming to replicate Temu's low-price advantage through direct sourcing and combining with FBA delivery. However, market analysts believe that the launch of Amazon Haul could distract from Amazon's core business focus. Over the years, Amazon has relied on a fast and convenient shopping experience to build its brand advantage, and the introduction of a low-cost mall may run counter to its efficient performance model, and it is difficult to truly shake Temu's market position.
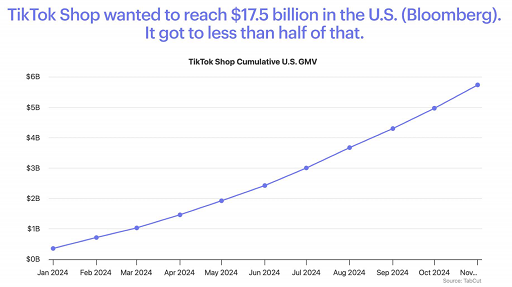
TikTok Shop, as another market rookie, officially entered the US market in September last year and has risen rapidly with the advantages of live streaming and social e-commerce. Although the platform fell short of its $17.5 billion sales target, it has become the largest social e-commerce platform in the United States. TikTok Shop initially only allowed local stores in the United States, and then gradually relaxed restrictions to introduce a large number of Chinese sellers. Despite the risk of a ban on TikTok in the United States, many brands and sellers have continued to invest in trying to seize the early stage of the market's expansion.

At the same time, regulatory pressure is accelerating. The US government announced in September that it would tighten the tax exemption policy for small packages, aiming to crack down on platforms that use the "small exemption" rule to import cheap goods in large quantities. The move will challenge platforms such as Temu, which rely on cheap cross-border direct sales, forcing them to rely more on local inventory. In addition, some countries have also strengthened the supervision of direct selling platforms, limiting the inflow of low-priced goods, with stricter supervision, China's direct selling model may gradually fade out.
The rise of the direct-selling model in China has also sparked controversy over quality issues, product safety, environmental impact, tax loopholes and the impact on local jobs. Although consumers are generally aware of these issues, many still choose to ignore them and continue to pursue price advantages. Although some of the goods on Amazon are essentially the same as those on Temu platform, the price is naturally higher than Temu due to the higher delivery costs, tariffs and brand protection costs borne by the platform, and consumers' acceptance and evaluation of these goods are also different.
The bottom line is that the U.S. e-commerce market is undergoing a new round of change. While Chinese platforms such as Temu and Shein have reshaped the market landscape with extreme low prices and flexible supply chains, platforms such as Amazon and TikTok are trying to maintain a competitive edge through differentiation. With the tightening of regulatory policies, the gradual localization of supply chains, and the increasing competition in the market, the future direction of the e-commerce industry remains to be seen.
III. The growth of e-commerce slowed down, and the giants accelerated to strengthen their competitive advantages
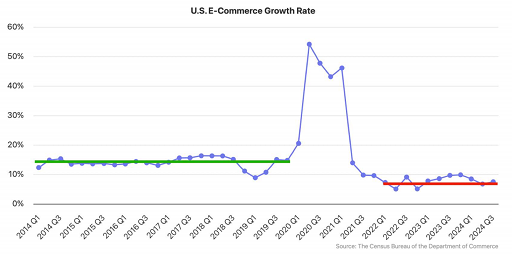
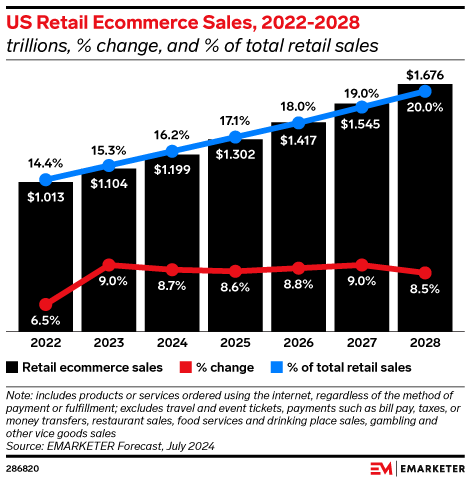
At present, the US e-commerce market is experiencing a sustained downturn, and the growth rate is far less than that of the past decade. During the epidemic, driven by home consumption, US e-commerce had recorded double-digit growth for several quarters, and with the intensiveness of inflationary pressure and slowing consumer demand, the current growth rate of e-commerce has dropped significantly, or even halved from the growth rate before the epidemic.
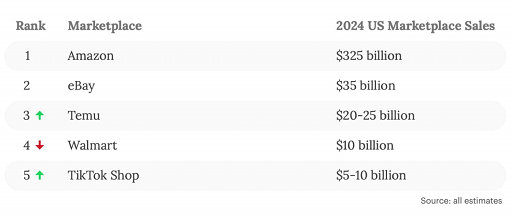
Despite sluggish growth in the overall market, industry leaders continue to expand against the trend. Amazon, Walmart, Temu, Shein, and TikTok Shop already account for more than half of the growth in the e-commerce market. While Amazon and Walmart have long been the preferred channels for sellers in the U.S., emerging platforms Temu and Shein are rapidly expanding with ultra-low prices and flexible supply chains. In 2024, Temu outperformed Walmart even more, even though its seller base is almost entirely from China.
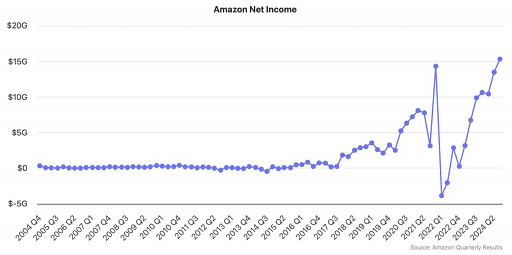
The e-commerce "winter" does not mean that all platforms are facing difficulties. As an industry giant, Amazon has achieved record profits by continuously increasing investment. Amazon CEO Andrew Jassy said same-day delivery is becoming one of Amazon's most competitive advantages and one of its lowest-cost delivery methods. In the last quarter, more than 40 million Amazon customers took advantage of free same-day delivery, an increase of more than 25% year-on-year. As the logistics network continues to improve, Amazon is further widening the gap with competitors.
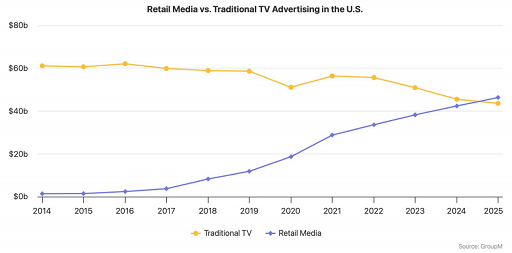
In addition, the advertising business has become an important pillar of Amazon's profitability. With more than $50 billion in annual advertising sales, it is one of Amazon's highest-margin businesses. As the retail media advertising market expands, overall retail media advertising spending in the United States is expected to surpass traditional TV advertising spending by 2025, further reflecting the competitiveness of e-commerce platforms in the advertising space.
Unlike Amazon, Walmart's core strength lies in its extensive network of offline stores, which are particularly dominant in the grocery sector. Doug McMillon, Walmart's chief executive, noted that in the past 12 months, the company has achieved same-day or next-day delivery of 4.4 billion items in the United States, with about 20 percent of those items delivered within three hours. By improving distribution efficiency and reducing costs, Walmart is meeting consumers' demand for convenience with an efficient grocery supply chain and strengthening its market competitiveness.
IV: AI reshapes the e-commerce experience, and online shopping continues to deepen
While the core "what to buy" of the retail industry has not fundamentally changed, "how to buy" is being gradually reshaped by emerging technologies such as AI. AI technology brings new shopping experiences, and although the current performance is not yet mature, its potential cannot be ignored.
Since July, Amazon's AI shopping assistant Rufus has been fully open in the United States, able to answer shopping questions such as purchase needs, product comparisons, and make suggestions based on the content of the conversation. However, such AI systems still have many problems, such as failure to accurately recommend the lowest price, lack of professionalism in selection, and even occasionally generate random results, reflecting that AI is not yet mature in product recommendation and accurate matching.
But in any case, the disruptive potential brought by AI has begun to emerge. Unlike traditional searches for "running shoes," AI is able to respond to more specific needs, such as "finding the best running shoes for marathons under 3 hours," greatly simplifying the decision-making process. However, historical experience shows that innovative concepts such as voice shopping and virtual reality have not fully fulfilled their promises in Western markets, and it remains to be seen whether AI shopping can really be popularized.
In recent years, the core logic of the e-commerce business model has not undergone revolutionary changes. The major platforms are still committed to finding room for growth, optimizing channel layout, and improving profit margins. The giants expand their share by constantly adapting to market changes, while smes face greater challenges. The US Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has also pointed out that Amazon's market dominance has increased competitive pressure and further compressed the space for new entrants.
At the same time, the division of platforms is becoming clearer. Content platforms such as TikTok, Instagram, and YouTube drive the desire to buy by creating demand, while trading platforms such as Amazon, Walmart, and Temu directly satisfy the need to buy. Some platforms such as TikTok and Instagram are also trying to deeply integrate content and transactions, creating a closed-loop consumption path of "from planting grass to pulling grass", and further strengthening the habit of "seeing and buying".
Although online shopping will not completely replace offline consumption, its penetration rate continues to increase, and more and more demand and shopping behavior are driven by online content. From AI recommendations to content planting to cross-platform transactions, the future of e-commerce will revolve around "intelligence" and "online". How to deeply combine technological innovation with consumer experience will become the key competitiveness of this industry.